Retail
Materiality summary
Leading the top half of the materiality table are customer issues:
- The health impact of products, especially for food retailers
- Credit affordability and treating customers fairly for credit retailers
- Ethical advertising and product labelling
- Equitable access to products and services
- Consumer ID protection and data privacy for all retailers, except for cash retailers
Governance issues, including board balance and effectiveness, leadership selection and preparation, and remuneration and incentives are all critical for companies exposed to key-man risk at leadership level.
Fair labour, external societal risks of doing business in Africa and industry equity obligations complete the top half of the materiality table.
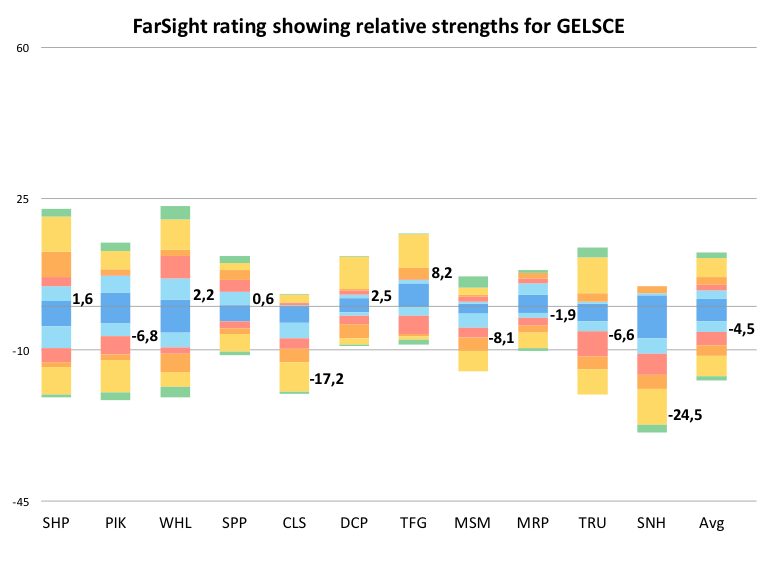
Results
Overall leadership maturity in the retail sector poor in comparison with the hospitals and pharmaceuticals, though somewhat better than food processors.
Particular weaknesses across the sector included board governance (TFG excepted), fair treatment of labour and talent management (WHL excepted) and, for food retailers, consideration of poor nutritional value/obesogenic foods.
General and apparel retailers scored worse than food retailers, though TFG top-scored, largely on account of the transparency and maturity of its reporting on board governance (including leadership succession) and its response to customer issues.
DCP significantly outperformed CLS, though the format of the listing statement, on which it was rated, demands a more disciplined and transparent approach.
While WHL and SHP top scored on the positive axis, they both show vulnerabilities too. WHL tends towards insincerity, while SHP tends towards disinterest. Both PIK and WHL tend to believe their own PR.
See the executive summary for individual company scores and materiality weightings. Buy our full report for detailed analysis and substantiation of our analysis.